Internal DHCP Virtual Network in Virtualbox
This post will cover practical example on how to run Internal Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Virtual Network in CentOS,Kali Linux and Windows in Virtualbox . It shows how to set Virtualbox and check the Guest OS communication in the virtual network and Wide Area Network (WAN).
In a nutshell, Internal Virtual Network settings will allow Guest Operating System (OS) run as a real computer internally within virtual network.Guest Operating System (OS) will able to communicate between each other but can't communicate with outside world (internet) or Wide Area Network (WAN) .
The testing that had been done for this tutorial is using virtualbox dhcpserver function. Virtualbox dhcpserver will assign the IP addresses for each Guest OS . Once Guest OS is set to run in similar network name , Internal Virtual Network will wire automatically. Virtualbox will automatically load the network driver ,assign IP address to each Guest OS and act as a complete network switch .
Below is the environment that I use for this tutorial
- Ethernet/Wireless router
- Ubuntu ( Host running on Virtualbox )
- Kali Linux (Guest OS 1)
- CentOS (Guest OS 2)
- Windows(Guest OS 3)
Internal Virtual Network Diagram
Below is the network topology for Virtualbox Internal DHCP Virtual Network.Kali Linux, CentOS and Windows connection only happens virtually where there is no physical wiring between them.IP addresses will be assigned by Virtualbox DHCP server.
Since the IP addresses are assigned by Virtualbox DHCP server , you will have different IP addresses than what I get in this tutorial.
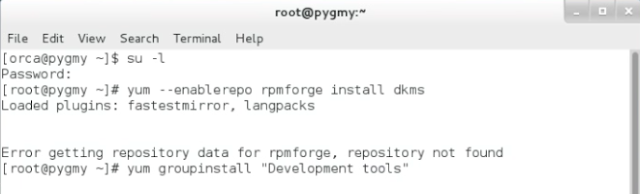
1) Enable Virtualbox DHCP server in the host.)
1.1) To enable the DHCP server, you need to enable it via command line in host machine. The preceding command will configured below details on your system.
Network name : Pentestlab
DHCP server IP address : 10.10.10.1
Network mask : 255.255.255.0
Guest OS lower IP address : 10.10.10.2
Guest OS upper IP address : 10.10.10.10
2) Internal Network Virtualbox settings .
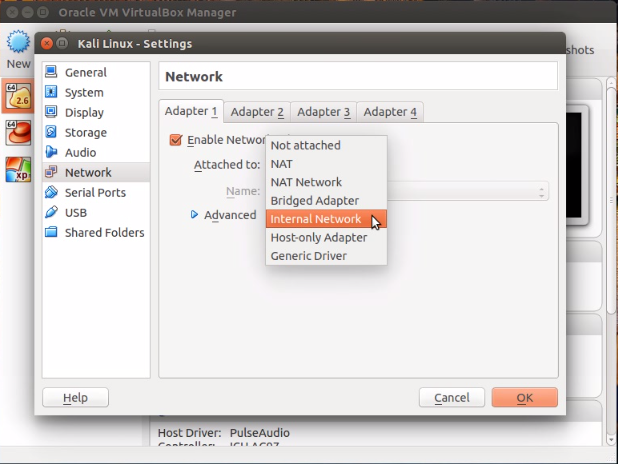
2.1) Go to "Settings>Network>Adapter 1" and attached the adapter to Internal Network.
2.2) Assign the network name for your guest OS. In this example, I have set and configured (in 1.1) my internal network name to "Pentestlab" .Configure the same network name as what is configured in Virtualbox host.
All three Guest OS have the same settings as I show above.
3) Run Guest Operating System (OS) and test the network.
Run CentOS,Windows and Kali Linux Virtual Machines.
3.1) DHCP server will assign each Guest OS IP address automatically . Below is IP addresses assign to my Guest OS machine.
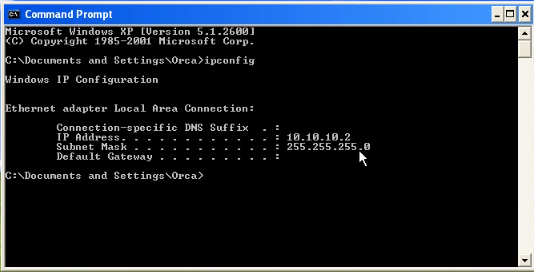
Windows : 10.10.10.2
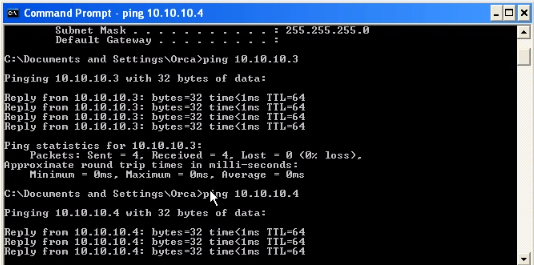
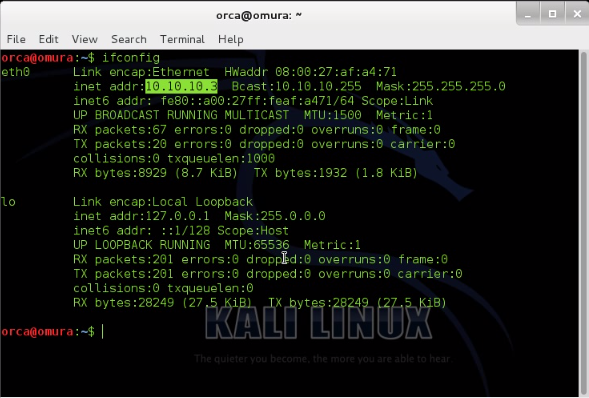
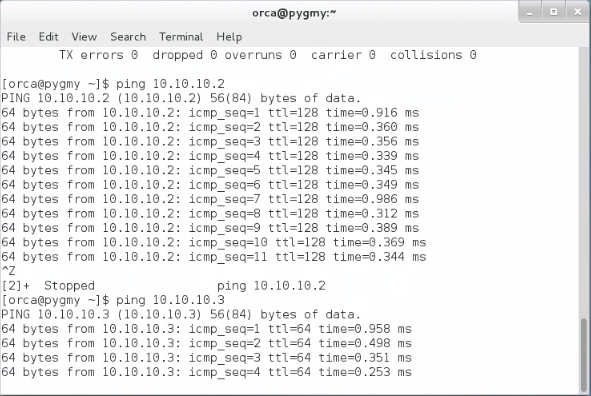
Kali Linux : 10.10.10.3
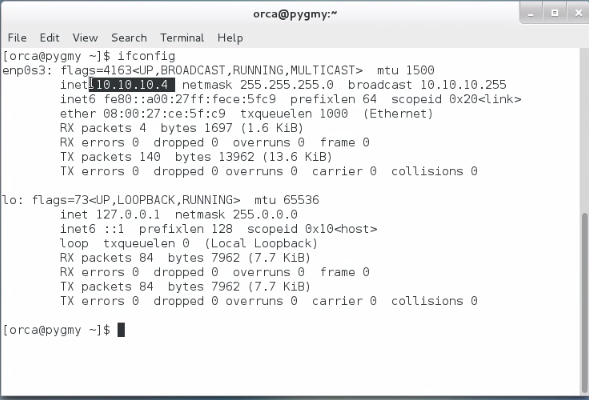
CentOS : 10.10.10.4
3.2) Display Windows IP address and send ping packet to Kali Linux (10.10.10.3) and CentOS (10.10.10.4) to make sure they are connected.
3.3) Display Kali Linux IP address and send ping packet to Windows (10.10.10.2) and CentOS (10.10.10.4) to make sure they are connected.
3.4) Display CentOS IP address and send ping packet to Windows (10.10.10.2) and Kali Linux (10.10.10.3) to make sure they are connected.
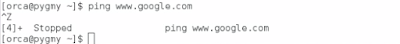
3.5) Browse/ping any domain in the internet to check the connection to Internet/WAN.
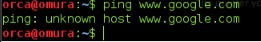 |
| Kali Linux unable to ping google |
 |
| CentOS unable to ping google |
 |
| Windows unable to browse Internet |
By default, in Internal DHCP Virtual Network, all three Guest OS must be able to communicate with each other but not to Wide Area Network (WAN) or the internet.
Conclusion.
- Internal Virtual Network configuration will allow guest OS connect to each other and are limited within the host configured network.
- Guest OS are not able to connect to Internet/Wide Area Network (WAN) .
- Advantage of using this setting is It is easy to setup and reduce the hassle of configuring each static IP addresses for multiple computer in lab network.
- No outside real world connection makes it easy to do real world testing in a secure environment .
For more information on this topic,please visit here